universal functions
ndarrayの全ての要素に対して基本的な計算を実行する。
以下オペランドが1つの単項universal functions。
abs,sqrt,square,exp,log,sign,ceil,floor,rint,modf,isnan,sin,cos,arcsin,arccosなどがある。
array = np.arange(10)
print(array)
# [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
sqrt = np.sqrt(array)
print(sqrt)
# [0. 1. 1.41421356 1.73205081 2. 2.23606798
# 2.44948974 2.64575131 2.82842712 3. ]
exp = np.exp(array)
print(exp)
# [1.00000000e+00 2.71828183e+00 7.38905610e+00 2.00855369e+01
# 5.45981500e+01 1.48413159e+02 4.03428793e+02 1.09663316e+03
# 2.98095799e+03 8.10308393e+03]
以下、オペランドが2つの2項universal functions。
いずれかのうち最大の値を残すmaximum()。
add,subtract,divide,power,maximum,minimum,copysign,greater,lessなどがある。
x = np.random.randn(10)
y = np.random.randn(10)
print(x)
# [ 1.3213258 0.12423666 -1.45665939 -1.49766467 -0.6129116 2.00056744
# -0.00816571 0.63247747 0.29497652 0.80000291]
print(y)
# [-0.76739214 0.95151629 0.03208859 0.40641677 0.82635027 1.01773826
# 0.75601178 0.25200147 1.59929321 0.6251983 ]
z = np.maximum(x,y)
print(z)
# [1.3213258 0.95151629 0.03208859 0.40641677 0.82635027 2.00056744
# 0.75601178 0.63247747 1.59929321 0.80000291]
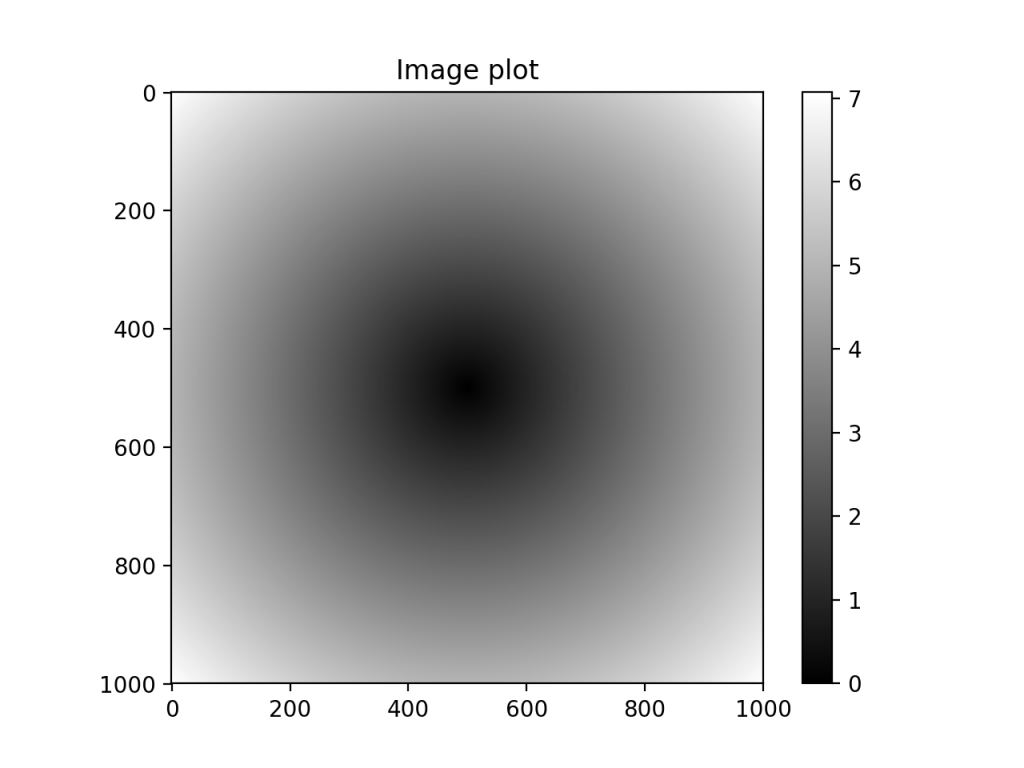
matplotlibにndarrayを引数として渡せば簡単にプロットできる。
\(z=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)をプロットしてみる。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
points = np.arange(-5,5,0.01)
xs,ys = np.meshgrid(points,points)
z = np.sqrt(xs**2 +ys**2)
plt.imshow(z, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.colorbar()
plt.title("Image plot")
plt.show()
3項演算子 where
マスクの論理値に従って2つのndarrayのうちいずれかの値を選択してリストに書く。
3項演算子を使ってPythonのlistに入れる方法は以下。
xa,xbはndarrayだが最終的なr1はPythonオブジェクト。
import numpy as np
xa = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
xb = np.array([6,7,8,9,10])
cnd = np.array([True,True,False,False,False])
r1 = [(x if c else y) for x,y,c in zip(xa,xb,cnd)]
print(r1)
対して、ndarrayに対して直に3項演算子を実行するwhereがある。
import numpy as np
xa = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
xb = np.array([6,7,8,9,10])
cnd = np.array([True,True,False,False,False])
r2 = np.where(cnd,xa,xb)
print(r2)
数学関数,統計関数,次元削減
\(n\)次のndarrayをある軸について集計して\(n-1\)次のndarrayにする。
集計方法としていくつかの数学関数、統計関数が用意されている。
以下5×4(2次)のndarrayについて、それぞれの列について平均を取り4列(1次)のndarrayにしている。
さらに列の平均を取りスカラーにしている。
import numpy as np
ary = np.random.randn(5,4)
print(ary)
# [[-1.84573174 1.84169514 1.43012623 -0.5416877 ]
# [-1.03660701 0.63504086 -0.12239017 -0.77822113]
# [ 0.1711323 -0.16660851 -0.7928288 1.17582814]
# [-0.29302267 -0.23316282 1.70611457 0.53870384]
# [-0.46513289 -1.12207588 0.01930695 0.49635739]]
print(ary.mean(axis=0))
# [-0.6938724 0.19097776 0.44806576 0.17819611]
print(ary.mean(axis=1))
# [ 0.22110048 -0.32554436 0.09688078 0.42965823 -0.26788611]
print(ary.mean())
# 0.030841804893752683